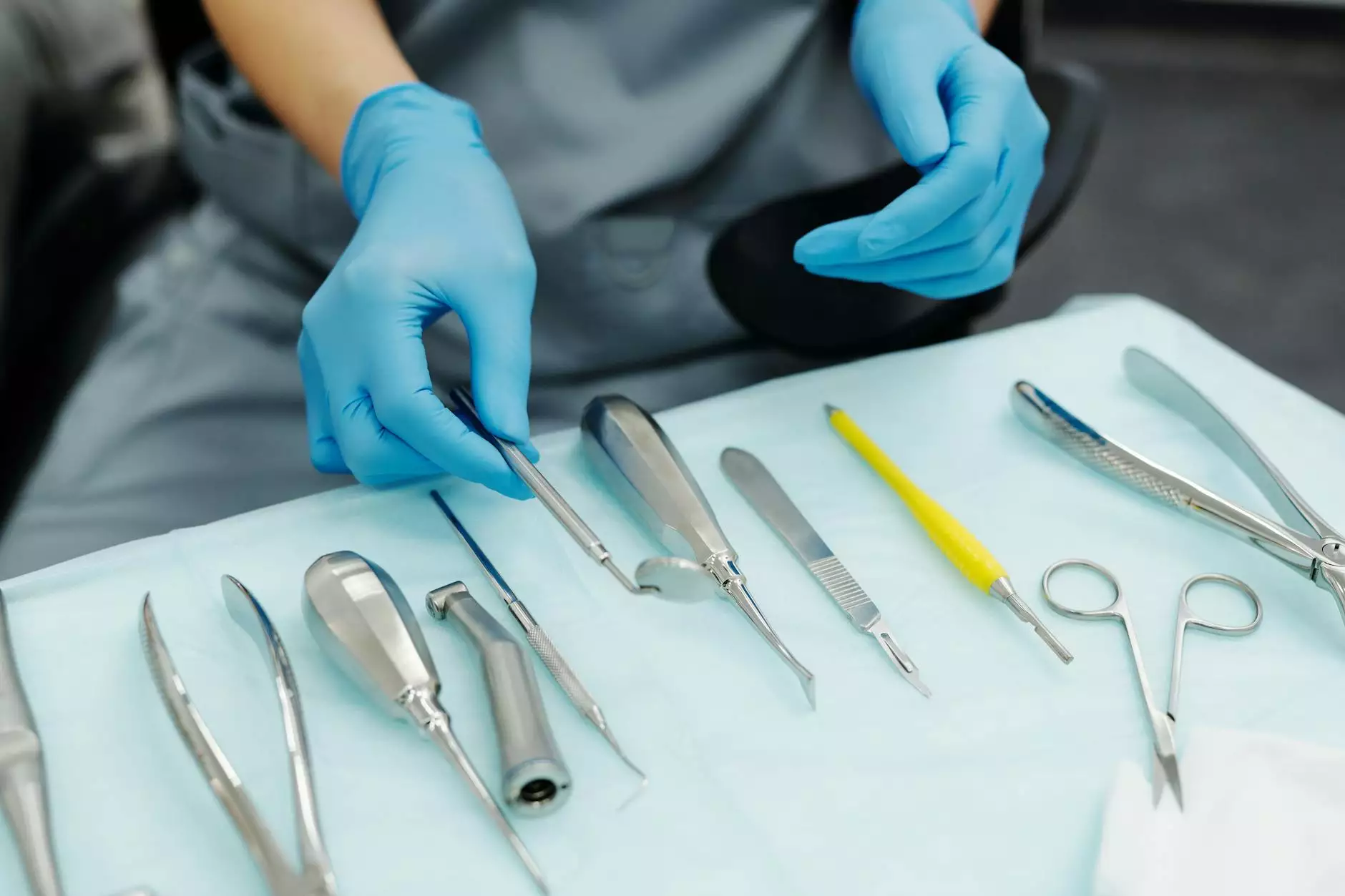
Orthopedic Surgical Instruments: Essential Tools for Modern Medicine

In the field of orthopedics, surgical instruments play a vital role in ensuring successful outcomes for patients. As a cornerstone of health & medical practice, these instruments are specifically designed to assist in surgical procedures that treat conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. Understanding these tools is crucial for both medical professionals and patients alike. Here, we delve into the various types of orthopedic surgical instruments, their applications, and their significance in modern medicine.
The Importance of Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
The role of surgical instruments in orthopedics cannot be overstated. They are fundamental for the following reasons:
- Precision: Orthopedic surgeries often require high levels of accuracy, and the right instruments enable surgeons to operate with precision.
- Efficiency: Specialized tools improve the speed of surgical procedures, leading to shorter operation times and reduced anesthesia exposure.
- Patient Safety: High-quality instruments minimize risks, enhance safety, and improve overall surgical outcomes.
- Versatility: Different types of instruments are designed to handle a range of orthopedic issues, from fractures to joint replacements.
Categories of Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
Orthopedic surgical instruments can be categorized based on their specific functions. Here are the primary categories:
1. Cutting Instruments
Cutting instruments are essential for making incisions in tissue or bone. They include:
- Scalpels: Used for precise incisions.
- Bone Saws: Employed for sawing through bone during procedures like joint replacements.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors are used for cutting tissue and sutures.
2. Grasping Instruments
These instruments are designed to hold or manipulate tissues during surgery. Examples include:
- Forceps: Designed to grasp tissues or hold structures.
- Tissue Holders: Specifically designed to stabilize tissues during intricate procedures.
3. Fixation Devices
Fixation devices are crucial for stabilizing bones. They include:
- Screws: Used to hold bones together during healing.
- Plates: Metal plates provide support and alignment for fractured bones.
- Nails: Intramedullary nails stabilize fractures within the bone.
4. Retractors
Retractors are used to hold back tissues, providing visibility and access to the surgical area:
- Self-retaining Retractors: These hold themselves in place, allowing hands-free operation.
- Hand-held Retractors: These require a surgical assistant to hold them in place.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
Choosing the appropriate orthopedic surgical instruments is paramount for successful surgical outcomes. Consider the following factors:
1. Quality and Durability
Invest in instruments made from high-quality materials. Stainless steel is often preferred for its strength, resistance to corrosion, and ease of sterilization. Quality instruments, like those from new-medinstruments.com, should withstand repeated use without losing functionality.
2. Functionality
Each surgical procedure has specific requirements. Surgeons must understand the functionality of each instrument and how it integrates into their surgical technique.
3. Ergonomics
Instruments should be designed for ease of use. Ergonomically designed handles can reduce hand fatigue during prolonged procedures.
Best Practices in Using Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
Using orthopedic surgical instruments correctly is crucial for successful surgical outcomes. Here are best practices that should be adhered to:
1. Proper Sterilization
Instruments must be sterilized before every use to eliminate the risk of infection. Follow hospital protocols for sterilization, which often include:
- Cleaning with enzymatic cleaners.
- Autoclaving for sterilization.
- Regular maintenance to ensure that instruments remain in optimal condition.
2. Training and Specialization
Medical professionals should undergo extensive training on how to use various orthopedic surgical instruments. Specialization in the type of surgery being performed can enhance proficiency.
3. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Regularly inspect and maintain surgical instruments to ensure they are functioning correctly. Broken or dull instruments can lead to complications during surgeries.
Innovations in Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
The field of orthopedics continues to evolve with technological advancements. Here are some notable innovations:
1. Minimally Invasive Instruments
Advances in technology have led to the development of instruments designed for minimally invasive surgeries. These instruments reduce patient recovery time and minimize tissue damage.
2. Robotics and Automation
Robotic-assisted surgery is becoming increasingly popular in orthopedic procedures. Instruments designed for robotic platforms enhance precision and allow for more complex operations to be performed with greater accuracy.
3. Smart Instruments
The integration of smart technology into surgical instruments allows for real-time data analysis and feedback during surgeries, improving outcomes and safety.
Conclusion: The Future of Orthopedic Surgical Instruments
As we move forward, the importance of orthopedic surgical instruments in healthcare continues to grow. With ongoing innovations and improvements in technology, the future holds promise for even more effective and efficient surgical practices. Surgeons, healthcare providers, and patients alike will benefit from the advancements in the functionality and efficacy of these essential tools. Investing in quality instruments, such as those available at new-medinstruments.com, will ensure that healthcare practices can meet the challenges of modern medicine effectively.
By understanding the significance, selection, and best practices surrounding orthopedic surgical instruments, we can contribute to better healthcare outcomes for all patients. The right instruments not only enhance surgical skill but also improve patient safety and recovery, ensuring that the future of orthopedic surgery is bright and filled with possibilities.